Research Interests
The Modelling and Simulation (M&S) group led by Prof
Wentong Cai has been conducting impactful research in M&S over two
decades. The group has published
extensively in top venues in the area such as ACM TOMACS, SMPT (Elsevier), IEEE TPDS, FGCS
(Elsevier), JPDC (Elsevier), and ACM SIGSIM PADS and
has won 14 Best Paper Awards in international conferences. Recent ones include WSC’22, ACM SIGSIMPADS’21, WSC’20, IEEE/ACM DS-RT’18, ACM SIGSIM PADS’18, and ACM SIGSIM PADS’17. Many alumni of the group now work as
Professors in leading universities in Europe and China or Research Engineers in
leading IT companies world-wide such as Microsoft, Alibaba, Tencent, and
Huawei.
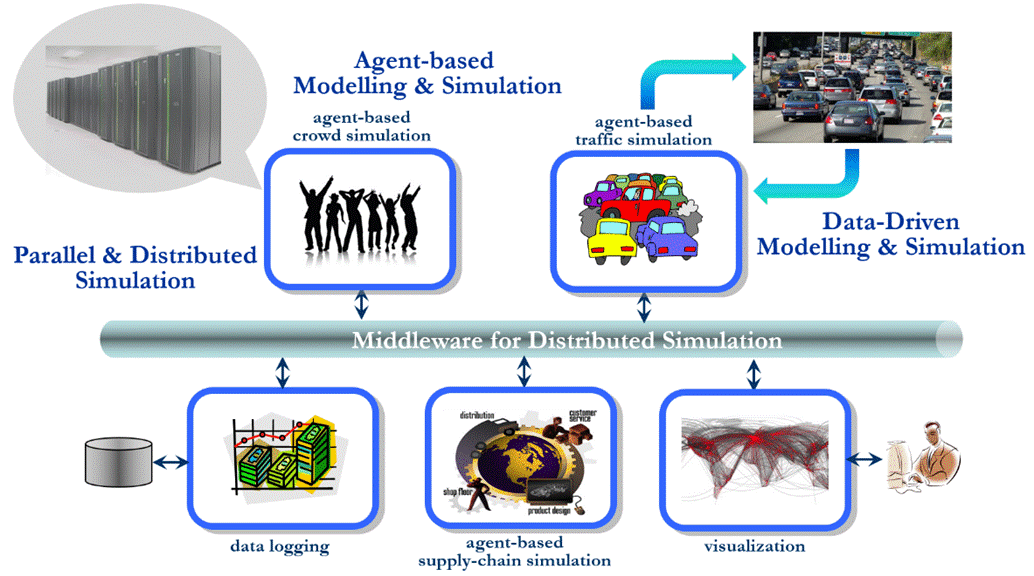
The research of the group mainly focuses on the
intersection between Computer Science and M&S. The current research interests include:
performance and scalability of discrete event simulation, large-scale distributed
virtual environment and cloud gaming, dynamic data-driven modelling and
simulation, and agent-based simulation applications (e.g., crowd and traffic
simulation).
a. Performance and Scalability of Discrete-Event Simulations
Over the last two decades, the research group has been
actively working on design and analysis of architecture, framework, and
protocols to support parallel & distributed simulation, focusing mainly on
performance and scalability issues.
We have conducted substantial research on time synchronization methods
for parallel and distributed simulations [a1, a4, a6, a8, a13, a15] and
performance optimization techniques for parallel and distributed simulation on
emerging computing platforms (such as Grid [a2, a5] and Cloud [a9, a10]) and
using hardware accelerators (such as GPU [a11, a16, a23] and FPGA [a21,
a22]). In recent years, we have
also studied the partitioning problem of large-scale agent-based simulations,
such as crowd [a7], traffic [a12], and social network simulation [a17]. Furthermore, to support efficient
simulation-based “what-if” analysis, we have developed simulation
cloning techniques for distributed simulation [a3] and agent-based simulation
on GPU [a14]. Techniques to
dynamically switch model abstraction to speed-up simulation execution were also
explored [a18-a20].
a1. Wentong
Cai, Stephen J. Turner, Bu Sung Lee and Junlan Zhou.
“An
Alternative Time Management Mechanism for Distributed Simulations”, ACM Transactions on
Modeling and Computer Simulation (TOMACS), Vol.15,
No.2, pp.1-29, April 2005.
a2. Yong
Xie, Yong Meng Teo, Wentong Cai, and Stephen J. Turner, “Service
Provisioning for HLA-based Distributed Simulation on the Grid”, in
Proceedings of the 19th IEEE/ACM/SCS Workshop on Principles of
Advanced and Distributed Simulation (PADS 2005), pp.282-291, Monterey,
California, USA, June 2005.
a3. Dan Chen, Stephen J.
Turner, and Wentong Cai, “Algorithms for HLA-based Distributed Simulation Cloning”,
ACM Transactions on Modeling
and Computer Simulation (TOMACS), Vol.15, No.4, pp.316-345, Oct 2005.
a4. Ke
Pan, Stephen J. Turner, Wentong Cai, and Zengxiang
Li, “A Hybrid HLA Time Management Algorithm Based on Both Conditional and
unconditional Information”, in Procs. of 22nd IEEE/ACM/SCS
Workshop on Principles of Advanced and Distributed Simulation (PADS 2008), pp.
203-211, Rome, Italy, 3-6 June 2008.
a5. Dan
Chen, Georgios K. Theodoropoulos, Stephen J. Turner, Wentong Cai, Robert
Minson, and Yi Zhang, “Large Scale Agent-based Simulation on the
Grid”, Future Generation Computer
Systems (FGCS), Vol.24, No.7, pp.658-671, July 2008.
a6. Dan Chen, Stephen J.
Turner, Wentong Cai, Georgios K Theodoropoulos, Muzhou
Xiong, and Michael Lees, “Synchronization in Federation Community
Networks”, Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing (JPDC), Vol.70, Issue 2, pp. 144-159, Feb 2010.
a7. Yongwei Wang, Michael Lees, and
Wentong Cai, “Grid-based partitioning for large-scale distributed
agent-based crowd simulation”, Proceedings of 2012 Winter
Simulation Conference (WSC 2012), Berlin, Germany, Dec 2012.
a8. Zengxiang Li, Wentong Cai, and Stephen J. Turner,
“Un-identical Federate Replication Structure for Improving Performance of
HLA-based Simulations”, Simulation Modeling Practice and Theory, Vol. 48, No. 11, pp.
112-128, Nov 2014.
a9. Daniel
Zehe, Alois Knoll, Wentong Cai, and Heiko Aydt, “SEMSim
Cloud Service: Large-Scale Urban Systems Simulation in the Cloud”, Simulation Modeling
Practice and Theory, Vol.58, No.2, pp.157-171, Nov 2015.
a10. Zengxiang Li, Wentong Cai, Stephen J. Turner, Xiaorong Li,
Ta Nguyen Binh Duong, Rick Siow Mong Goh, “Adaptive Resource
Provisioning Mechanism in VEEs for Improving Performance of HLA-based
Simulations”, ACM Transactions
on Modeling and Computer Simulation (TOMACS),
Vol. 26, No.1, Dec 2015.
a11. Xiasong Li, Wentong Cai, and Stephen J. Turner,
“Supporting Efficient Execution of Large-scale Agent-based Simulation on
GPU”, Concurrency and Computation:
Practice and Experience, Vol.28, No.12, pp.3313-3332, 2016
a12. Yadong Xu, Wentong Cai, David Eckhoff, Suraj Nair, Alois
Knoll, “A Graph Partitioning Algorithm for
Parallel Agent-based Road Traffic Simulation”, in Proceedings of 31st ACM SIGSIM Conference on Principles
of Advanced Discrete Simulation (SIGSIM PADS 2017), Singapore, 24-26 May 2017.
a13. Yadong Xu, Wentong Cai, Heiko Aydt, Michael Lees, and
Daniel Zehe, “Relaxing Synchronization in Parallel Agent-based Road Traffic
Simulation”, in ACM
Transactions on Modeling and Computer Simulation
(TOMACS), Vol.27, No. 2, May 2017.
a14. Xiaosong Li, Wentong Cai, Stephen J. Turner, “Cloning Agent-based
Simulation”, in ACM
Transactions on Modeling and Computer Simulation
(TOMACS), Vol.27, No.2, May 2017.
a15. Yadong Xu, Vaisagh Viswanathan,
and Wentong Cai, “Reducing Synchronization Overhead with Computation
Replication in Parallel Agent-based Road Traffic Simulation”, in IEEE Transactions on Parallel and
Distributed Systems (TPDS), Vol.28, No.11, pp.3286-3297, Nov 2017.
a16. Nguyen Quang Anh, Rui Fan, and Wentong Cai.
“Optimizing Agent-based Simulations for the GPU”, in Proceedings of
2018 International Conference on High Performance Computing and Simulation
(HPCS 2018), Orleans, France, 16-20 July 2018.
a17. Yulin Wu, Wentong Cai, Zengxiang Li, Wen Jun Tan, and Xiangting
Hou. “Efficient Parallel Simulation over Large-scale Social Contact
Networks”, in ACM Transactions on Modeling and Computer Simulation (TOMACS),
29(2):10:1-10:25, 2019.
a18. Philipp Andelfinger, Yadong Xu, David Eckhoff, Wentong Cai, and Alois Knoll, “Fidelity and Performance of
State Fast-Forwarding in Microscopic Traffic Simulations”, ACM Transactions on Modelling and Computer
Simulation (TOMACS), 30(2): 10:1-10:26, 2020.
a19. Philipp Andelfinger, David
Eckhoff, Wentong Cai and Alois Knoll, “Fast-Forwarding of Vehicle
Clusters in Microscopic Traffic Simulations”, in Procs. of ACM SIGSIM
Conference on Principles of Advanced Discrete Simulation (PADS 2020), Miami,
Florida, 15-17 June 2020.
a20. Moon Gi Seok, Wentong
Cai, Hessam S. Sarjoushian, and Daejin Park,
“Adaptive Abstract-level Conversion Framework for Accelerated
Discrete-event Simulation in Smart Semiconductor Manufacturing”, in IEEE
Access, 8:165247-165262, 2020.
a21. Jiajian Xiao,
Görkem Kılınç, Philipp
Andelfinger, David Eckhoff, Wentong Cai and Alois Knoll, “Pedal to the
Bare Metal: Road Traffic Simulation on FPGAs Using High-Level Synthesis”,
in Procs. of ACM SIGSIM Conference on Principles of Advanced Discrete
Simulation (PADS 2020), Miami, Florida, 15-17 June 2020.
a22. Jiajian Xiao, Philipp
Andelfinger, Wentong Cai, Paul Richmond, Alois Knoll, David Eckhoff. “OpenABLext: An Automatic Code Generation Framework for
Agent-based Simulations on CPU-GPU-FPGA Heterogenous Platforms”, in Concurrency
and Computation: Practice and Experience, 32(21), 2020.
a23.
Quang Anh Pham Nguyen,
Philipp Andelfinger, Wen Jun Tan, Wentong Cai, Alois Knoll,
“Transitioning Spiking Neural Network Simulators to Heterogeneous
Hardware”, in ACM Transactions on
Modelling and Computer Simulation (TOMACS), Vol.31, No.2, April 2021.
b. Large-scale Distributed Virtual Environments and Cloud
Gaming
The central theme of our research in this area is to investigate how to maintain the interactivity and consistency of a large-scale, highly interactive media environment under the constraints of large network latency and huge resource demands. Fundamental problems, such as consistency [b1], server provisioning and placement [b2], zone mapping [b4], and update scheduling [b3] have been investigated. In recent years, we have also conducted research on server provisioning [b9] and player request dispatching and server allocation [b6, b7, b8, b10, b11] for Cloud Gaming. A set of toolkits for cross-platform Cloud Gaming that is able to utilize elastic resources on public clouds has also been developed [b5].
b1. Suiping Zhou, Wentong Cai,
Bu-Sung Lee, and Stephen J Turner, “Time-space consistency in large-scale
distributed virtual environments”, ACM Transactions on
Modeling and Computer Simulation (TOMACS), Volume 14, Issue 1,
pp.31-47, Jan 2004.
b2. Duong Ta, Thang Nguyen, Suiping Zhou, Xueyan Tang, Wentong Cai, and Rassul Ayani, “Interactivity-Constrained Server Provisioning in Large-Scale Distributed Virtual Environments”, IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems (TPDS), Vol.23, No.2, pp.304-312, Feb 2012.
b3. Yusen
Li, Wentong Cai, “Update Schedules for Improving Consistency in
Multi-server Distributed Virtual Environments Journal of Network and Computer
Applications”, Journal of Network
and Computer Applications, Vol.41, pp.263-273, May 2014.
b4. Yusen
Li and Wentong Cai, “Consistency-aware Zone Mapping and Client Assignment
in Multi-server Distributed Virtual Environments”, IEEE Transactions on Parallel
and Distributed Systems (TPDS) Vol. 26, No.6, pp.1570 – 1579, June
2015.
b5. Yusen Li, Yunhua Deng, Ronald Seet, Xueyan Tang,
and Wentong Cai, “MASTER: Multi-platform Application Streaming Toolkits for
Elastic Resources”, in Proceedings of ACM Multimedia 2015, Brisbane,
Australia, 26-30 Oct 2015.
b6. Yusen
Li, Xueyan Tang, and Wentong Cai, “Play Request Dispatching for Efficient
Virtual Machine Usage in Cloud Gaming”, IEEE Trans. on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology (TCSVT).
Vol.25, No.12, pp.2052-2063, Dec 2015.
b7. Yusen
Li, Xueyan Tang, and Wentong Cai, “Dynamic Bin Packing for On-Demand
Cloud Resource Allocation”, IEEE
Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems (TPDS), Vol.27, No.1,
pp.157-170, Jan 2016.
b8. Yunhua Deng, Yusen Li,
Xueyan Tang, and Wentong Cai, “Server Allocation
for Multiplayer Cloud Gaming”, in Proceedings of 2016 ACM Multimedia,
pp.918-927, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 15-19 Oct 2016.
b9. Yusen
Li, Yunhua Deng, Xueyan Tang, Wentong Cai, Xiaoguang
Liu and Gang Wang, “On Server Provisioning for Cloud Gaming”, in
Proceedings of 2017 ACM Multimedia, Mountain View, CA, USA, 23-27 Oct 2017.
b10. Iryanto Jaya, Wentong
Cai, Yusen Li. “Rendering Server Allocation for MMORPG Players in Cloud
Gaming”, in Procs. of 49th International Conference on
Parallel Processing (ICPP 2020), Edmonton, AB, Canada, 17-20 August 2020.
b11. Iryanto Jaya, Yusen Li, and Wentong Cai. “Minimizing
Play Request Rejection through Workload Splitting in Edge-Cloud Gaming”,
in Procs. of 2021 IEEE International Conference on Parallel and Distributed
Systems (ICPADS 2021), Beijing, China, 14-16 Dec 2021.
c. Dynamic Data-Driven Modelling and Simulation
Our early work in this area was mainly on symbiotic
simulation [c1]. Our recent work
focuses on exploring
the synergy amongst dynamic data-driven techniques, data analytics, and agent-based modelling and simulation. To this end, we have carried out
research using data-driven approach for agent-based model calibration [c3, c8,
c10] and model creation [c2, c4, c5, c6, c7]. Traditional methods to create
agent-based model require in-depth domain knowledge and involve a great amount
of manual efforts. Our work has
shown that it is possible to use data analytics to extract useful knowledge and
insight from the data to facilitate model development for agent-based
simulation. Specifically, a survey
on data-driven crowd modelling techniques can be found in [c11]. In addition, we have also developed a
framework for “just-in-time” analysis of the simulation data to
infer the usefulness (or utility) of a simulation run [c9]. It can be used to reduce overall
resource utilization of an agent-based simulation study which often involves a
large number of simulation runs (an ensemble of simulations).
c1. Heiko
Aydt, Stephen J. Turner, Wentong Cai, and Malcolm Yoke Hean Low, “An
Agent-based Generic Framework for Symbiotic Simulation”, in Adelinde M.
Uhrmacher and Danney Weyns edited, Agents, Simulation and Applications,
published by Taylor and Francis, June 2009.
c2. Jinghui Zhong, Linbo Luo, Wentong Cai, and
Michael Lees, “Automatic Rule Identification for Agent-Based Crowd Models
through Gene Expression Programming”, in Proceedings of 13th
International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems (AAMAS
2014), pp.1125-1132, Paris, France,
May 2014.
c3. Jinghui
Zhong, Nan Hu, Wentong Cai, Michael Lees, Linbo Luo, “Density-Based
.Evolutionary Framework for Crowd Model Calibration”, Journal of Computational Science, Vol.6,
No1. pp. 11-22, Jan 2015.
c4. Jinghui
Zhong, Wentong Cai, Linbo Luo, and Haiyan Yin, “Learning Behaviour
Patterns from Video: A Data-driven Framework for Agent-based Crowd
Modelling”, in Proceedings of the 14th International
Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems (AAMAS 2015),
pp.801-809, Istanbul, Turkey, May 2015.
c5. Jinghui
Zhong, Wentong Cai, Michael Lees, Linbo Luo, and Nan Hu, “Automatic Model
Construction for the Behaviour of Human Crowds”, in Applied Soft Computing, Vol.56, pp.368-378, July 2017.
c6. Mingbi
Zhao, Wentong Cai, and Stephen J. Turner, “CLUST: Simulating Realistic
Crowd Behavior by Mining Pattern from Crowd
Videos”, in Computer Graphics Forum,
Vol. 37, Issue 1, pp.184-201, Feb 2018.
c7. Mingbi Zhao, Jinghui
Zhong, and Wentong Cai, “A Role-dependent Data-driven Approach for High Density Crowd
Behaviour Modelling”, in ACM
Transactions on Modelling and Computer Simulation (TOMACS), Vol.28, No.4,
Oct 2018.
c8. Philipp Andelfinger, Yihao Chen, Daniel Zehe,
Boyi Su, David Eckhoff, Wentong Cai, and Alois Knoll. “Incremental
Calibration on Agent-based Pedestrian Models Using Human-in-the-Loop
Simulation”, in Proceedings of 2018 Winter Simulation Conference (WSC
2018), Gothenburg, Sweden, 9-12 Dec 2018.
c9. Philipp Andelfinger, Sajeev Udayakumar, David Eckhoff, Wentong Cai, and
Alois Knoll. “Model Pre-emption based on Dynamic Analysis of Simulation
Data to Accelerate Traffic Light Optimization”, in Proceedings of 2018
Winter Simulation Conference (WSC 2018), Gothenburg, Sweden, 9-12 Dec 2018.
c10. Htet
Naing, Wentong Cai, Nan Hu, Tiantian Wu, and Liang
Yu. “Data-driven Microscopic Traffic Modelling and Simulation using
Dynamic LSTM”, in Procs. of ACM SIGSIM Conference on Principles of
Advanced Discrete Simulation (PADS 2021), Suffolk,
Virginia, May 31-June 2, 2021
c11. Jinghui
Zhong, Dongrui Li, Zhixing
Huang, Chengyu Lu, and Wentong Cai, “Data-Driven Crowd Modeling Techniques: A Survey”, to appear in ACM Transactions on Modelling and Computer
Simulation (TOMACS).
d. Agent-based Simulation Applications
Our research also concerns with using agent-based
modelling and simulation to understand the effect of individual behaviour on
system-level dynamics and to develop decision support systems for planning and
tactical operations. To support
crowd simulation [d1], we have developed a generic framework for human
behavioural modelling, which aims to model how humans make decisions in time
critical real-life situations.
Particularly, the framework takes into account how a person’s
decision making process is affected by experiences, emotion and other
people’s behaviour [d2, d3].
The framework has been used to create crowd scenarios in various applications
(such as serious games [d4], evacuation analysis [d5, d14], crowd control [d9],
capacity planning [d10], and transportation research [d12, d13]). Other agent-based simulation
applications include: traffic simulation [d6, d7] and supply-chain simulation [d8,
d11]. More information about our
work on agent-based crowd modelling and simulation can be found here.
d1. Suiping Zhou, Dan Chen, Wentong Cai, Linbo Luo, Malcolm
Yoke Hean Low, Feng Tian, Darren Ong, Benjamin Hamilton, “Crowd Modelling and
Simulation Technologies”, ACM
Transactions on Modelling and Computer Simulation (TOMACS), Volume 20,
Issue 4, October 2010.
d2. Linbo
Luo, Suiping Zhou, Wentong Cai, Michael Lees, Malcolm
Yoke Hean Low, and Kabilen Sornum, “HumDPM: A
decision process model for modelling human-like behaviour in time-critical and
uncertain situations”, Trans on Computational Science, XII, Vol
6670, pp. 206-230, 2011.
d3. Heiko
Aydt, Michael Lees, Linbo Luo, Wentong
Cai, Malcolm Yoke Hean Low, and Sornum Kabilen Kadirvenlen,
“A computational model of emotions for agent-based crowds in serious
games”, in Proceedings of 2011 IEEE/WIC/ACM International Conferences on
Intelligent Agent Technology (IAT 2011), Lyon, France, August 2011.
d4. Linbo Luo, Haiyan
Yi, Jinghui Zhong, Wentong Cai, Michael Lees, and Suiping Zhou,
“Mission-Based
Scenario Modelling and Generation for Virtual Training”, in Proceedings
of 9th Annual AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence and
Interactive Digital Entertainment (AIIDE 2013), Boston, USA, Oct
2013.
d5. Jinghui Zhong, Wentong
Cai, and Linbo Luo, “Crowd Evacuation Planning Using Cartensian
Genetic Programming and Agent-based Crowd Modelling”, in Proceedings of
2015 Winter Simulation Conference (WSC 2015), Huntington Beach, California,
USA, 6-9 Dec 2015.
d6. Abhinav Sunderrajan, Vaisagh Viswanathan, Wentong Cai, and Alois Knoll,
“Data Driven Adaptive Traffic Simulation of an Expressway”, in
Proceedings of 2016 Winter Simulation Conference, pp.1194-1205, Washington DC,
USA, 11-14 Dec 2016.
d7. Wen Jun Tan, Wentong
Cai, and Allan Zhang, “Integration
Design of Supply Chain Hybrid Simulation”, in Proceedings of 2017 Winter
Simulation Conference (WSC 2017), Las Vegas, 3-6 Dec 2017.
d8. Philipp Andelfinger, Yadong
Xu, Wentong Cai, David Eckhoff, and Alois Knoll, “Fast Forwarding
Agent States to Accelerate Microscopic Traffic Simulation”, in
Proceedings of 32nd
ACM SIGSIM Conference on Principles of Advanced Discrete Simulation (SIGSIM
PADS 2018), Rome, 23-25 May 2018. (Best
Paper Award)
d9. Nan
Hu, Jinghui Zhong, Joey Tianyi Zhou, Suiping Zhou,
Wentong Cai, and Christopher Monterola, “Guide Them Through: An Automatic
Crowd Control Framework Using Multi-objective Genetic Programming”, in Applied Soft Computing, Vol.66,
pp.90-103, May 2018.
d10. Sing Kuang Tan, Nan Hu, and Wentong Cai, “A Data-driven Path
Planning Model for Crowd Capacity Analysis”, in Journal of Computational Science (Elsevier), Vol. 34, pp.66-70,
May, 2019.
d11. Wen June
Tan, Wentong Cai, and Allan Zhang, "Structural-aware Simulation Analysis
of Supply Chain Resilience", in International
Journal of Production Research. 58(17):5175-5195,
2020.
d12. Boyi Su, Philipp Andelfinger, Jaeyoung
Kwak, David Eckhoff, Henriette Cornet, Coran Marinkovic, Wentong Cai, and Alois
Knoll. “A Passenger Model for Simulating Boarding and Alighting in
Spatially Confined Transportation Scenarios”, in Journal of
Computational Science, 45:101173, 2020
d13. Michael Wagner, Philipp Andelfinger,
Henriett Cornet, Wentong Cai, Alois Knoll, and David Echhoff.
“Evaluation of Guidance Systems at Dynamic Public Transport Hubs Using
Crowd Simulation”, in Procs. of 2020 Winter Simulation Conference,
Orlando, Florida, USA, 13-16 Dec 2020
d14. Boyi Su, Jaeyoung Kwak, Ahmad Reza
Pourghaderi, Michael H. Lees, Kenneth B. K. Tan, Shin Yi Loo, Ivan S. Y. Chua,
Joy L. J. Quah, Wentong Cai, and Marcus E. H. Ong. “A Model-based
Analysis of Evacuation Strategies in Hospital Emergency Departments”, in
Procs. of 2021 Winter Simulation Conference, Phoenix AZ, USA, 13-15 Dec
2021.