|
Recent projects undertaken at NTU
|
|
·
Capturing
Waste with Waste: Continuous Carbon Capture Using Highly Efficient Sorbents
Derived from Incineration Ashes (New)
|
|
·
“Breaking
the Ground” in Semakau Landfill: Technological Solutions for Site
Investigation and Material Reuse (new)
|
|
·
Clean
Syngas from Waste for Electricity and Chemicals (new)
|
|
·
Development of an
In-line Pre-formed Chloramine System for Biofouling Control in Seawater
Reverse Osmosis Desalination Process (new)
|
|
·
Long-Term
Environmental Behavior for Treated Incineration
Bottom Ash
|
|
·
Investigation
and Optimisation of Ozone Ceramic Membrane Process
|
|
·
Improving
Photocatalysts to Recycle Microplastics to Fuels by Artificial Intelligence
|
|
·
Zero-Liquid Discharge from Water Reclamation through Hybrid
Multiplex Catalytic Oxidation Process
·
Advanced Combustion and Corrosion Control System for Steam
Boilers in WtE Gasification Plants
·
Nitrogen-Doped TIO2-Activated Carbon (AC) Composite
for Adsorptive Photocatalytic Oxidation-Reduction of Refractory Organic
Substances Under Solar Irradiation in Water Purification
·
Controlled Synthesis of Catalytic Polyoxometalates for the
Removal of Phenol from Waste Water
·
Gasification-based Syngas Upgrading and Purification System for
Enhanced Power Generation
·
A Novel Approach to Reutilize Incineration Bottom Ash (IBA) for
Civil Engineering Applications: IBA Aerated Concrete
·
Effective Techniques for Quick Response to Oil Spillage on
Singapore Roads
·
Sustainable Materials: Green Avenues Towards High Value Products
·
Use of Copper Slag as a Land Reclamation Fill Material in
Singapore
|
|
|
|
|
Total research grant
My total
research grant received to date as Principal Investigator is S$6.5 millions (US$5.0 millions). In addition, I have also
involved as a co-Principal Investigator of several projects which received a
total research grant of S$18 millions.
|
|
|
|
R&D
projects for community improvement 
|
|
|
|
General summary of my
research fields
|
My research encompasses both practical
applications of environmental technologies and fundamental studies of
process mechanisms.
My core research areas of interest focus on advanced
oxidation processes for water and wastewater treatment, developing
innovative treatment technologies for water and soil pollution controls,
developing nanomaterials for environmental applications, waste-to-energy and waste-to-materials. My research approach
couples experimental investigations with use of geochemical models,
statistical tools, and advanced analytical equipment for analysis and
interpretation of the results. Brief summaries of my research projects and
the representative publications are listed below.
|
|
|
|
|
Advanced oxidation processes for water and
wastewater treatment
I have over 15 years of research track records in redox
technologies for surface water, wastewater and
groundwater treatment. For the oxidation technologies, my research activities
cover sulfate-radical based advanced oxidation
process or SR-AOP (homogeneous and heterogeneous), UV-based AOP (homogeneous
and heterogeneous), Fenton processes (heterogeneous), photocatalysis
(heterogeneous), electrochemical oxidation, and sonochemical
oxidation, and hybrid AOPs. On SR-AOP, my group has made significant
contribution to the scientific community in terms of advancing the
understanding of the mechanisms of the heterogeneous SR-AOP with metal oxides
(monometallic oxide and bimetallic oxides) and carbonaceous materials as
catalysts to activate peroxymonosulfate and
peroxydisulfate. We have discussed our works in our numerous scientific
papers and 3 critical reviews in the top journals. Specifically, we have provided insights into the
radical and non-radical reaction pathways associated with transformation and
mineralization of a wide range of organic emerging micropollutants such as
antibiotics, cytostatic drugs, bisphenol A and industrial chemicals (Oh et
al. 2016, Chen et al. 2018).
On the homogeneous SR-AOP, our group is among the leading contributor to
mitigation strategy for controlling iodinated disinfection
by-products such as iodinated trihalomethanes and iodoacids
in RO water (Xiao et al.
2015, 2016). Our group also developed composite catalytic materials which
comprise mixed metal oxides, bimetallic oxides, and catalyst-nanocarbon
composites that exhibit multifunctional properties such as combined
catalysis, adsorption-promoted catalysis, “switchable” catalysis, etc. Our
iron-based catalytic composites can function as Fenton catalyst, photo-Fenton
catalyst and photocatalyst, such that their applications can be switched over
the day/night cycle (Hu et al. 2014, 2015). When irradiated with sunlight,
they trigger sunlight-driven photocatalytic redox degradation of organic
pollutants without any chemical addition. The materials can be recovered from
the treated water using magnet. We have also developed a hybrid
TiO2-activated carbon composites, which can be used as solar-driven
photocatalyst (Yap et al., 2011) or solar-regenerable activate carbon (Yap
and Lim 2012). This invention has been approved for PCT filing
(PCT/SG2014/000273) as a recognition of our intellectual property.
|
|
1.
|
Bao Y., Oh W.D., Lim T.T.*, Wang R., Webster R.D., Hu
X.* (2019). Elucidation of stoichiometric efficiency, radical generation and transformation pathway during
catalytically oxidation of sulfamethoxazole via peroxymonosulfate
activation. Water Research 151, 64-74.
|
|
2.
|
Oh W.D.*, Lim T.T.* (2019). Design and application of heterogeneous
catalysts as peroxydisulfate activator for organics removal: An overview. Chemical
Engineering Journal 358, 110-133.
|
|
3.
|
Oh W.D.*, Chang V.W.C., Lim T.T.* (2019). A comprehensive
performance evaluation of heterogeneous Bi2Fe4O9/peroxymonosulfate system for sulfamethoxazole
degradation. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 26, 1026-1035.
|
|
4.
|
Zhang Y., Lim T.T.* (2018).
Chapter 12 Photodegradation of cytostatic drugs in low-pressure UV
photoreactor through direct and indirect pathways. In Fate and Effects of
Cytostatic Pharmaceuticals in the Environment. Eds. Heath E., Filipič
M., Kosjek T., Isidori
M. In press. Springer.
|
|
5.
|
Bao Y., Oh W.D., Lim T.T.*, Wang R., Webster R.W.,
Hu X.* (2018). Surface-nucleated heterogeneous growth of zeolitic
imidazolate framework-A unique precursor towards catalytic ceramic
membranes: synthesis, characterization and
organics degradation. Chemical Engineering Journal 353, 69-79.
|
|
6.
|
Bao
Y., Lim T.T., Wang R., Webster
R.D., Hu X.* (2018). Urea-assisted one-step synthesis of cobalt ferrite
impregnated ceramic membrane for sulfamethoxazole degradation via peroxymonosulfate activation. Chemical Engineering
Journal 343, 737-747.
|
|
7.
|
Chen
X., Oh W.D., Hu Z.T., Sun Y.M., Webster R.D., Li S.Z., Lim T.T.* (2018). Enhancing sulfacetamide degradation by peroxymonosulfate activation with N-doped graphene
produced through delicately-controlled nitrogen
functionalization via tweaking thermal annealing processes. Applied
Catalysis B: Environmental 225, 243–257.
|
|
8.
|
Hu
Z.T.*, Oh W.D., Liu Y., Yang E.H., Lim
T.T.* (2018). Controllable mullite bismuth ferrite micro/nanostructures
with multifarious catalytic activities for switchable/hybrid catalytic
degradation processes. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 509,
502-514.
|
|
9.
|
Oh
W.D., Dong Z., Goei R., Lim T.T.*
(2017). Surface-active bismuth ferrite as superior peroxymonosulfate
activator for aqueous sulfamethoxazole removal: Performance, mechanism and quantification of sulfate
radical. Journal of Hazardous Materials 325, 71-81.
|
|
10.
|
Zhang
Y., Zhang J., Xiao Y., Chang V.W.C., Lim
T.T.* (2017). Direct and indirect photodegradation pathways of
cytostatic drugs under UV germicidal irradiation: process kinetics and
influences of water matrix species and oxidant dosing. Journal of Hazardous
Materials 324, 481-488.
|
|
11.
|
Oh
W.D.*, Dong Z., Lim T.T. (2017).
Hierarchically-structured Co–CuBi2O4and Cu–CuBi2O4
for sulfanilamide removal via peroxymonosulfate activation. Catalysis Today 280, 2-7.
|
|
12.
|
Zhang
Y., Xiao Y., Zhang J., Chang V.W.C., Lim
T.T.* (2017). Degradation of cyclophosphamide and 5-fluorouracil in
water using UV and UV/H2O2: kinetics investigation, pathways and energetic analysis. Journal of Environmental Chemical
Engineering 5(1), 1133-1139.
|
|
13.
|
Wu
W., Huang Z.H., Hu Z.-T., He C., Lim
T.T.* (2017). High performance duplex-structured SnO2 anode
modified by SnO2-Sb-CNT composite for bisphenol A removal:
Electrochemical oxidation enhanced by adsorption. Separation and
Purification Technology 179, 25-35.
|
|
14.
|
Oh
W.D.*, Chang V.W.C., Hu Z.T., Goei R., Lim T.T.* (2017). Enhancing the
catalytic activity of g-C3N4 through Me doping (Me =
Cu, Co and Fe) for selective sulfathiazole
degradation via redox-based advanced oxidation process. Chemical
Engineering Journal 323, 260-269.
|
|
15.
|
Zhang
Y., Zhang J., Xiao Y., Chang V.W.C., Lim
T.T.* (2016). Kinetic and mechanistic investigation of azathioprine
degradation in water by UV, UV/H2O2 and
UV/persulfate. Chemical Engineering Journal 302, 526–534.
|
|
16.
|
Oh
W.D., Dong Z., Lim T.T.* (2016).
Generation of sulfate radical through
heterogeneous catalysis for organic contaminants removal: Current
development, challenges and prospects. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental 194, 169–201.
|
|
17.
|
Xiao Y., Zhang L., Zhang W., Lim K.Y., Webster R.D., Lim T.T.* (2016).
Comparative evaluation of iodoacids removal by
UV/persulfate and UV/H2O2 processes. Water Research.
102, 629-639.
|
|
18.
|
Wu
W., Huang Z.H., Lim T.T.*
(2016). A comparative study on electrochemical oxidation of bisphenol A by
boron-doped diamond anode and modified SnO2-Sb anodes:
influencing parameters and reaction pathways. Journal of Environmental
Chemical Engineering 4, 2807-2815.
|
|
19.
|
Hu
Z.T., Chen Z., Goei R., Wu W., Lim
T.T.* (2016). Magnetically recyclable Bi/Fe-based hierarchical
nanostructures via self-assembly for environmental decontamination.
Nanoscale 8, 12736-12746.
|
|
20.
|
Oh
W.D., Lua S.K., Dong Z., Lim T.T.*
(2016). Fabrication of three-dimensional hierarchically-structured
CuBi2O4 composites via kinetic control for versatile
application in water treatment. Nanoscale 8, 2046 – 2054.
|
|
21.
|
Lua
S.K., Oh W.D., Zhang L.Z., Yao L., Lim
T.T., Dong Z.* (2015). A molybdovanadophosphate-based
surfactant encapsulated heteropolyanion with
multi-lamellar nano-structure for catalytic wet
air oxidation of organic pollutant under ambient conditions. RSC Advances 5
(115), pp. 94743-94751.
|
|
22.
|
Oh W.D., Dong Z., Hu Z., Lim
T.T.* (2015). A novel
quasi-cubic CuFe2O4–Fe2O3 prepared at low temperature for enhanced
oxidation of bisphenol A via peroxymonosulfate
activation. Journal of Materials Chemistry A 3, 22208-22217.
|
|
23.
|
Hu Z.T., Lua S.K., Lim
T.T.* (2015). Cuboid-like Bi2Fe4O9/Ag
with graphene-wrapping tribrid composite with
superior capability for environmental decontamination: Nanoscaled
material design and visible-light-driven multifunctional catalyst. ACS
Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering 3 (11), pp. 2726-2736.
|
|
24.
|
Hu Z.T., Lua S.K., Yan X., Lim T.T.* (2015). Nanostructured hexahedron of
bismuth ferrite clusters: delicate synthesis processes and an efficient
multiplex catalyst for organic pollutant degradation. RSC Advances 5,
86891–86900.
|
|
25.
|
Oh W.D., Lua S.K., Dong Z., Lim T.T.* (2015). A novel
three-dimensional spherical CuBi2O4 nanocolumn arrays
with persulfate and peroxymonosulfate
activation functionalities for 1H-benzotriazole removal. Nanoscale 7(17),
8149-8158.
|
|
26.
|
Wu W., Huang Z., Lim
T.T.* (2015). Enhanced electrochemical oxidation of
phenol using hydrophobic TiO2-NTs/SnO2-Sb-PTFE
electrode prepared by pulse electrodeposition. RSC Advances 5, 32245-32255.
|
|
27.
|
Xiao Y., Zhang L., Yue J., Webster R.D., Lim T.T.* (2015). Kinetic modeling
and energy efficiency of UV/H2O2 treatment of iodinated trihalomethanes
Water Research 75, 259-269.
|
|
28.
|
Oh W.D., Lua S.K., Dong Z., Lim T.T.* (2015). Performance of magnetic activated
carbon composite as peroxymonosulfate activator
and regenerable adsorbent via sulfate
radical-mediated oxidation processes. Journal of Hazardous Materials
284(2), 1-9.
|
|
29.
|
Oh W.D., Lua S.K., Dong Z., Lim T.T.* (2014). High surface area DPA-hematite for
efficient detoxification of bisphenol A via peroxymonosulfate
activation. Journal of
Materials Chemistry A 38, 15836-15845.
|
|
30.
|
Hu
Z-T, Chen B., Lim T.T.* (2014).
Single-crystalline Bi2Fe4O9 synthesized by
low-temperature co-precipitation: Performance as photo- and Fenton
catalysts. RSC Advances 4, 27820–27829.
|
|
31.
|
Zhou
T.*, Wu X., Mao J., Zhang Y., Lim
T.T. (2014). Rapid degradation of sulfonamides
in a novel heterogeneous sonophotochemical
magnetite-catalyzed Fenton-like (US/UV/Fe3O4/Oxalate)
system. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental
160-161, 325-334.
|
|
32.
|
Wu W., Huang Z., Lim T.T.* (2014). Recent development of mixed metal
oxide anodes for electrochemical oxidation of organic pollutants in water. Applied
Catalysis A: General 480, 58-78.
|
|
33.
|
Xiao Y., Fan R., Zhang L., Yue J., Webster R.D., Lim T.T.* (2014). Photodegradation
of iodinated trihalomethanes in aqueous solution by UV 254 irradiation.
Water Research 49, 275-285.
|
|
34.
|
Zhou T.*, Wu X., Zhang Y., Li J., Lim T.T.* (2013). Synergistic catalytic degradation of
antibiotic sulfamethazine in a heterogeneous sonophotolytic
goethite/oxalate Fenton-like system. Applied
Catalysis B: Environmental 136– 137, 294–301.
|
|
35.
|
Yap P.S., Lim T.T.*
(2012). Solar regeneration of powdered activated carbon impregnated with
visible-light responsive photocatalyst: factors affecting performances and
predictive model. Water Research 46, 3054-3064.
|
|
36.
|
Zhou T.*, Lim T.T.*,
Wu X. (2011). Sonophotolytic degradation of azo
dye reactive black 5 in a ultrasound/UV/ferric
system and the roles of different organic ligands. Water Research 45(9), 2915-2924.
|
|
37.
|
Zhou T., Lim T.T.*, Chin S.S., Fane A.G.
(2011). Treatment of organics in reverse osmosis concentrate from a
municipal wastewater reclamation plant: Feasibility test of advanced
oxidation processes with/without pretreatment.
Chemical Engineering Journal 166, 932-939.
|
|
38.
|
Zhou T.*, Lu X., Lim T.T., Li
Y., Wong F.S. (2010). Degradation of chlorophenols (CPs) in an
ultrasound-irradiated Fenton-like system at ambient circumstance: The QSPR
(quantitative structure–property relationship) study. Chemical Engineering Journal
156, 347–352.
|
|
39.
|
Zhou T.*, Lim T.T.*,
Li Y., Lu X.,
and Wong F.S. (2010). The role and fate of EDTA in
ultrasound-enhanced zero-valent iron / air system. Chemosphere 78, 576–582.
|
|
40.
|
Zhou T.*, Lim T.T.,
Lu X., Li Y., Wong F.S. (2009). Simultaneous degradation of 4CP and EDTA in
a heterogeneous ultrasound/Fenton like system at ambient circumstance. Separation and Purification Technology 68
(3), 367-374.
|
|
|
|
Photocatalysis
|
|
1.
|
Bao
Y., Lim T.T., Goei R., Zhong Z.,
Wang R., Hu X.* (2018). One-step construction of heterostructured
metal-organics@Bi2O3 with
improved photoinduced charge transfer and enhanced activity in
photocatalytic degradation of sulfamethoxazole under solar light
irradiation. Chemosphere 205, 396-403.
|
|
2.
|
Hu Z.-T.*, Liang Y.N., Zhao J., Zhang Y., Yang
E.-H., Chen J., Lim T.T.*
(2018). Ultra-effective integrated technologies for water disinfection with
a novel 0D-2D-3D nanostructured rGO-AgNP/Bi2Fe4O9
composite. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental 227, 548-556.
|
|
3.
|
Oh
W.D.*, Lok L.W., Veksha A., Giannis A., Lim T.T.* (2018). Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of
bisphenol A with Ag-decorated S-doped g-C3N4 under
solar irradiation: Performance and mechanistic studies. Chemical
Engineering Journal 333, 739-749.
|
|
4.
|
Nie
L, Liu G., Xie J., Lim T.T.,
Armatas G.S., Xu R., Zhang Q.* (2017). Syntheses,
crystal structures, and photocatalytic properties of two ammonium-directed
Ag−Sb−S complexes. Inorganic Chemistry Frontier 4, 954-959.
|
|
5.
|
Bao
Y., Lim T.T., Zhong Z., Wang R.,
Hu X.* (2017). Acetic acid-assisted fabrication of hierarchical flower-like
Bi2O3 for photocatalytic degradation of
sulfamethoxazole and rhodamine B under solar irradiation. Journal of
Colloid and Interface Science 505(1) 489-499.
|
|
6.
|
Hu
Z.T., Chen Z., Goei R., Wu W., Lim
T.T.* (2016). Magnetically recyclable Bi/Fe-based hierarchical
nanostructures via self-assembly for environmental decontamination.
Nanoscale 8, 12736-12746.
|
|
7.
|
Chen
Z.* and Lim T.T. (2016). Chapter
4 Nanostructured Catalytic and Adsorbent Materials for Water Remediation.
In 50 years of Materials Science in Singapore. Eds. Boey
F., Chowdari B.V.R., Venkatraman S.S. World
Scientific Publishing Ltd., pp 75-111.
|
|
8.
|
Yu
S., Liu J., Zhu W., Hu Z., Lim T.T.,
Yan X.* (2015). Facile room-temperature synthesis of carboxylated
graphene oxide-copper sulfide nanocomposite with
high photodegradation and disinfection activities under solar light
irradiation. Scientific Reports 5, 16369. doi:10.1038/srep16369.
|
|
9.
|
Hu Z.T., Lua S.K., Yan X., Lim T.T.* (2015). Nanostructured hexahedron of
bismuth ferrite clusters: delicate synthesis processes and an efficient
multiplex catalyst for organic pollutant degradation. RSC Advances 5,
86891–86900.
|
|
10.
|
Hu Z.T., Lua S.K., Lim
T.T.* (2015). Cuboid-like Bi2Fe4O9/Ag
with graphene-wrapping tribrid composite with
superior capability for environmental decontamination: Nanoscaled
material design and visible-light-driven multifunctional catalyst. ACS
Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering 3 (11), pp. 2726-2736.
|
|
11.
|
Hu
Z.T., Liu J., Yan X., Oh W.D., Lim
T.T.* (2015). Low-temperature synthesis of graphene/Bi2Fe4O9
composite for synergistic adsorption-photocatalytic degradation of
hydrophobic pollutant under solar irradiation. Chemical Engineering Journal
262, 1022–1032.
|
|
12.
|
Goei R., Lim
T.T.* (2014). Ag-decorated TiO2
photocatalytic membrane with hierarchical architecture: photocatalytic and
anti-bacterial activities. Water Research 59, 207–218.
|
|
13.
|
Hu Z-T, Chen B., Lim T.T.* (2014).
Single-crystalline Bi2Fe4O9 synthesized by
low-temperature co-precipitation: Performance as photo- and Fenton
catalysts. RSC Advances 4, 27820–27829.
|
|
14.
|
Goei R., Lim
T.T.* (2014). Asymmetric TiO2
hybrid photocatalytic ceramic membrane with porosity gradient: Effect of
structure directing agent on the resulting membranes architecture and
performances. Ceramics International 40, 6747-6757.
|
|
15.
|
Ronn G., Dong Z.L., Lim T.T.* (2013). High-permeability Pluronic-based
TiO2 hybrid photocatalytic membrane with hierarchical porosity:
fabrication, characterizations and performances.
Chemical Engineering Journal 228, 1030-1039.
|
|
16.
|
Wang P., Fane A. G., Lim T.T.* (2013). Evaluation of
a submerged membrane vis–LED photoreactor (sMPR)
for carbamazepine degradation and TiO2 separation. Chemical
Engineering Journal 215-216, 240–251.
|
|
17.
|
Han Z., Chang V.W.*, Wang X., Lim T.T., Lynn H. (2013). Experimental study on visible-light induced
photocatalytic oxidation of gaseous formaldehyde by polyester fiber supported photocatalysts. Chemical
Engineering Journal 218, 9-18.
|
|
18.
|
Wang X., Lim
T.T.* (2013). Highly
efficient and stable Ag-AgBr/TiO2
composites for destruction of E. coli under visible light irradiation.
Water Research 47 (12), pp. 4148-4158.
|
|
19.
|
Wang P., Tang Y., Dong Z., Chen Z., Lim T.T.* (2013). Ag–AgBr/TiO2/RGO nanocomposite for
visible–light photocatalytic degradation of penicillin G. Journal of
Materials Chemistry A 1, 4718–4727.
|
|
20.
|
Yap P.S., Cheah Y.L., Srinivasan M., Lim T.T.* (2012). Bimodal N-doped P25-TiO2/AC
composite: Preparation, characterization, physical stability, and
synergistic adsorptive-solar photocatalytic removal of sulfamethazine.
Applied Catalysis A: General 427–428, 125-136.
|
|
21.
|
Wang X., Tang Y., Chen Z., Lim T.T.* (2012). Highly stable heterostructured
Ag-AgBr/TiO2 composite: A bifunctional
visible-light active photocatalyst for destruction of ibuprofen and
bacteria. Journal of Materials Chemistry 22(43), 23149-23158.
|
|
22.
|
Hou D.X., Goei R., Wang X, Wang P., Lim T.T.* (2012). Preparation of carbon-sensitized and Fe-Er
codoped TiO2 with response surface methodology for bisphenol A
photocatalytic degradation under visible-light irradiation. Applied
Catalysis B: Environmental, 126, 121-133.
|
|
23.
|
Yap P.S., Lim T.T.*
(2012). Solar regeneration of powdered activated carbon impregnated
with visible-light responsive photocatalyst: factors affecting performances
and predictive model. Water Research 46, 3054-3064.
|
|
24.
|
Tang Y., Wee P., Lai Y., Wang X., Gong D., Kanhere
P.D., Lim T.T., Dong Z., Chen
Z.* (2012). Hierarchical TiO2
Nanoflakes and nanoparticles hybrid structure for improved
photocatalytic activity. Journal of Physical Chemistry C 116 (4), 2772–2780.
|
|
25.
|
Wang P., Lim T.T.*
(2012). Membrane vis-LED photoreactor for simultaneous penicillin G
degradation and TiO2 separation. Water Research 46(6), 1825-1837.
|
|
26.
|
Hou D., Feng L., Zhang J., Dong S.*, Zhou D., Lim T.T. (2012). Preparation, characterization and performance of a novel
visible light responsive spherical activated carbon-supported and Er3+:YFeO3-doped
TiO2 photocatalyst. Journal of Hazardous
Materials 199-200, 301-308.
|
|
27.
|
Wang X.P., Tang Y, Leiw M.Y., Lim T.T.* (2011). Solvothermal synthesis of Fe-C codoped
TiO2 nanoparticles for visible-light photocatalytic removal of
emerging organic contaminants in water. Applied Catalysis A: General 409–410, 257– 266.
|
|
28.
|
Wang P., Zhou T., Wang R., Lim T.T.* (2011). Carbon-sensitized and
nitrogen-doped TiO2 for photocatalytic degradation of sulfanilamide under visible-light irradiation. Water
Research 45, 5015-5026.
|
|
29.
|
Gao B.*, Yap P.S., Lim T.M., Lim T.T.* (2011). Adsorption-photocatalytic
degradation of acid red 88 by supported TiO2 :
Effect of activated carbon support and aqueous anions. Chemical
Engineering Journal 171, 1098-1107.
|
|
30.
|
Wang
X.P., Lim T.T.* (2011). Effect
of hexamethylenetetramine on the visible-light photocatalytic activity of
C-N codoped TiO2 for bisphenol A
degradation: evaluation of photocatalytic mechanism and solution toxicity.
Applied Catalysis A: General 399, 233-241.
|
|
31.
|
Wang P., Yap P.S., Lim
T.T.* (2011). C-N-S tridoped TiO2 for photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline under
visible-light irradiation. Applied Catalysis A: General 399, 252–261.
|
|
32.
|
Yap P.S., Lim T.T.*
(2011). Effect of aqueous matrix species on synergistic removal of
bisphenol-A under solar irradiation using nitrogen-doped TiO2/AC
composite. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental 101, 709-717.
|
|
33.
|
Yap P.S., Lim T.T.*,
Srinivasan M. (2011). Nitrogen-doped TiO2/AC
bi-functional composite prepared by two-stage calcination for enhanced
synergistic removal of hydrophobic pollutant using solar irradiation.
Catalysis Today 161, 46-52.
|
|
34.
|
Wang X.P., Lim T.T.*
(2010). Solvothermal synthesis of C-N codoped TiO2 and photocatalytic
evaluation for bisphenol A degradation using a
visible-light irradiated LED photoreactor. Applied Catalysis B:
Environmental. 100,
355-364.
|
|
35.
|
Lim T.T.*, Yap P.S., Srinivasan M., Fane A.G. (2010). TiO2/AC
composites for synergistic adsorption-photocatalysis processes: present
challenges and further developments for water treatment and
reclamation. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology 41(13),
1173 - 1230.
|
|
36.
|
Subagio D.P., Srinivasan M.*, Lim M., Lim T.T.* (2010). Photocatalytic degradation of Bisphenol-A by
nitrogen-doped TiO2 hollow sphere in a Vis-LED photoreactor. Applied
Catalysis B: Environmental 95, 414–422.
|
|
37.
|
Yap P.S., Lim T.T.*,
Lim M., Srinivasan M. (2010). Synthesis and characterization of
nitrogen-doped TiO2/AC composite for the
adsorption-photocatalytic degradation of aqueous bisphenol-A using solar
light. Catalysis Today 151, 8–13.
|
|
38.
|
Gao B.*, Lim T.M., Subagio D.P., Lim T.T.* (2010). Zr-doped TiO2 for enhanced
photocatalytic degradation of bisphenol A. Applied Catalysis A: General
375(1), 107-115.
|
|
|
Environmental nanomaterials for water/air
decontamination
|
Catalytic ceramic membrane for removing
recalcitrant organics
Over
the last 10 years, my group has advanced the research of coupling catalytic
oxidation and membrane separation process. The synergistic processes were
enabled through our catalytic ceramic membrane research. We developed three
types of such hybrid membranes: (1) photocatalytic membrane, (2) catalytic sulfate-radical oxidation membrane, and (3) catalytic
ozonation ceramic membrane. One of our inventions, Ag-decorated
photocatalytic TiO2-coated alumina membrane, has three functionalities:
antibacterial and antibiofouling property, photocatalytic, and separation
with pore sizes down to 4 nm (Goei and Lim 2014).
|
|
1.
|
Bao Y., Oh W.D., Lim T.T.*, Wang R., Webster R.W.,
Hu X.* (2018). Surface-nucleated heterogeneous growth of zeolitic
imidazolate framework-A unique precursor towards catalytic ceramic
membranes: synthesis, characterization and
organics degradation. Chemical Engineering Journal 353, 69-79.
|
|
2.
|
Bao Y., Lim T.T., Wang
R., Webster R.D., Hu X.* (2018). Urea-assisted one-step synthesis of cobalt
ferrite impregnated ceramic membrane for sulfamethoxazole degradation via peroxymonosulfate activation. Chemical Engineering
Journal 343, 737-747.
|
|
3.
|
Lim T.T.* and Goei R. (2016). Chapter 5
Combined Photocatalysis-Separation Processes for Water Treatment using
Hybrid Photocatalytic Membrane Reactors. In Photocatalysis: Applications.
Eds. Dionysiou D. D., Li Puma G., J. Ye, Schneider J., Bahnemann
D.. Royal Society of Chemistry, pp 130-156.
|
|
4.
|
Goei R., Lim
T.T.* (2014). Ag-decorated TiO2
photocatalytic membrane with hierarchical architecture: photocatalytic and
anti-bacterial activities. Water Research 59, 207–218.
|
|
5.
|
Goei R., Lim
T.T.* (2014). Asymmetric TiO2 hybrid
photocatalytic ceramic membrane with porosity gradient: Effect of structure
directing agent on the resulting membranes architecture and performances.
Ceramics International 40, 6747-6757.
|
|
6.
|
Ronn G., Dong Z.L., Lim T.T.* (2013). High-permeability Pluronic-based TiO2
hybrid photocatalytic membrane with hierarchical porosity: fabrication, characterizations and performances. Chemical Engineering
Journal 228, 1030-1039.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Zerovalent metal particles
|
|
1.
|
Kim
H.S., Kim T., Ahn J.Y., Hwang K.Y., Park J.Y., Lim T.T., Hwang I.* (2012). Aging characteristics and reactivity of two types of nanoscale
zero-valent iron particles (FeBH and
FeH2) in nitrate reduction. Chemical Engineering Journal 197, 16–23.
|
|
2.
|
Zhou T., Li Y., Lim
T.T.* (2010). Catalytic hydrodechlorination
of chlorophenols by Pd/Fe nanoparticles: Comparisons with other bimetallic
systems, kinetics and mechanism. Separation and Purification
Technology 76, 206-214.
|
|
3.
|
Lim T.T.* and Zhu B.W. (2009). Chapter 14: Practical applications of
bimetallic nanoiron particles for reductive
dehalogenation of haloorganics: prospects and
challenges. In Environmental Applications of Nanoscale and
Microscale Reactive Metal Particles. Eds. K.M.
Carvalho-Knighton and C. L. Geiger, ACS
Symposium Series, Vol. 1027, American Chemical
Society, USA, pp 245-261.
|
|
4.
|
Feng J., Zhu B.W., Lim
T.T.* (2008). Reduction of chlorinated methanes
with nano-scale Fe particles: Effects of amphiphiles on the dechlorination reaction and two-parameter regression
for kinetic prediction. Chemosphere 73,
1817–1823.
|
|
5.
|
Lim T.T.*, Zhu B.W. (2008). Effects of anions on the
kinetics and reactivity of nanoscale Pd/Fe in trichlorobenzene dechlorination. Chemosphere 73, 1471–1477.
|
|
6.
|
Zhu
B.W., Lim T.T.*, Feng J. (2008).
Influences of amphiphiles on dechlorination of a trichlorobenzene by nanoscale
Pd/Fe: Adsorption, reaction kinetics, and interfacial interactions. Environmental
Science & Technology 42,
4513–4519.
|
|
7.
|
Zhu B.W., Lim T.T.*
(2007). Catalytic
reduction of chlorobenzenes with Pd/Fe nanoparticles: reactive sites,
catalyst stability, particle ageing and regeneration. Environmental Science &
Technology 41, 7523-7529.
|
|
8.
|
Lim T.T.*, Feng J., Zhu B.W. (2007). Kinetic and mechanistic examinations of
reductive transformation pathways of brominated methanes
with nano-scale Fe and Ni/Fe particles. Water Research 41, 875-883.
|
|
9.
|
Feng J., Lim T.T.*
(2006). Iron-mediated
reduction rates and pathways of halogenated methanes
with nanoscale Pd/Fe: Analysis of linear free energy relationship. Chemosphere. Chemosphere
66(9), 1765-1774.
|
|
10.
|
Zhu
B.W., Lim T.T.*, Feng J. (2006).
Reductive dechlorination of
1,2,4-trichlorobenzene with palladized nanoscale
Fe0 particles supported on chitosan and silica. Chemosphere,
65(7), 1137-1145.
|
|
11.
|
Feng J., Lim T.T.*
(2005). Pathways
and kinetics of carbon tetrachloride and chloroform reductions by
nano-scale Fe and Fe/Ni particles: comparison with commercial micro-scale
Fe and Zn. Chemosphere
59(9), 1267-1277.
|
|
Nanosorbents
|
|
1.
|
Oh W.D.*, Lei J., Veksha A., Giannis A.,
Chan W.P., Lisak G., Lim T.T.*
(2018). Ni-Zn-based nanocomposite loaded on cordierite-mullite honeycomb
for syngas desulfurization: Performance evaluation and regeneration
studies. Chemical Engineering Journal 351, 230-239.
|
|
2.
|
Wu M.*, Chang B., Lim T.T., Oh W.D., Lei J., Mi J.* (2018). High-sulfur capacity and regenerable Zn-based sorbents
derived from layered double hydroxide for hot coal gas desulfurization. Journal of Hazardous Materials 360,
391-401.
|
|
3.
|
Wu M.*, Shi L., Lim T.T., Veksha A., Yu F., Fan H., Mi J.* (2018). Ordered
mesoporous Zn-based supported sorbent synthesized by a new method for
high-efficiency desulfurization of hot coal gas. Chemical Engineering
Journal 353, 273-287.
|
|
4.
|
Oh W.D.*, Lei J., Veksha A., Giannis A.,
Lisak G., Chang V.W.C., Hu X., Lim
T.T. * (2018). Influence of surface morphology on the performance of
nanostructured ZnO-loaded ceramic honeycomb for
syngas desulfurization. Fuel 211C, 591-599.
|
|
5.
|
Loo
S.L., Lim T.T., Krantz W.B.,
Fane A.G.*, Hu X. (2015). Potential evaluation and perspectives on using
sponge-like superabsorbent cryogels for onsite
water treatment in emergencies. Desalination and Water Treatment 53,
1506-1515.
|
|
6.
|
Loo
S.L., Fane A.G., Lim T.T.*,
Krantz W.B., Liang Y.N., Liu X., Hu X.* (2013). Superabsorbent cryogels decorated with silver nanoparticles as a novel
water technology for point-of-use disinfection, Environmental Science &
Technology 47(16), 9363-9371.
|
|
7.
|
Chen C.
P., Wang P. H., Lim T.T., Liu L.
H., Liu S. M., Xu R.* (2013). A facile synthesis of monodispersed
hierarchical layered double hydroxide on silica spheres for efficient
removal of pharmaceuticals from water. Journal of Materials Chemistry A 1,
3877–3880.
|
|
8.
|
Loo S.L., Krantz
W.B., Lim T.T., Fane
A.G.*, Hu X.* (2013). Design and synthesis of
ice-templated PSA cryogels for water
purification: Towards tailored morphology and properties. Soft Matter 9(1),
224–234.
|
|
9.
|
Wang B., Wu H., Yu L. Xu R., Lim T.T., Lou X.W.* (2012). Template-free formation of uniform
urchin-like a-FeOOH hollow spheres with
superior capability for water treatment. Advanced Materials 24(8), 1111-1116.
|
|
10.
|
Goh K.H., Lim T.T.* (2010).
Influences of co-existing species on the sorption of toxic
oxyanions from aqueous solution by nanocrystalline
Mg/Al layered double hydroxide. Journal of Hazardous Materials 180, 401-408.
|
|
11.
|
Goh K.H., Lim T.T.*,
Banas A., Dong Z.L. (2010). Sorption characteristics and mechanisms of
oxyanions and oxyhalides having different molecular properties on Mg/Al
layered double hydroxide nanoparticles.
Journal of Hazardous Materials 179 (1-3), 818-827.
|
|
12.
|
Goh K.H., Lim T.T.*,
Dong Z.L. (2010). Removal of
arsenate from aqueous solution by nanocrystalline Mg/Al layered double
hydroxide: sorption characteristics, prospects, and challenges. Water
Science & Technology 61(6), 1411-1417.
|
|
13.
|
Goh K.H., Lim
T.T.*, Dong Z.L. (2009). Enhanced arsenic removal by hydrothermally
treated nanocrystalline Mg/Al layered double hydroxide with nitrate
intercalation. Environmental Science & Technology 43, 2537–2543.
|
|
14.
|
Lim T.T.*, Goh K.H., Goei R., Dong Z.L. (2009).
Mechanistic and thermodynamic studies of oxyanion sorption by various
synthetic Mg/Al layered double hydroxides. Water Science & Technology
59(5), 1011-1017.
|
|
15.
|
Goh K.H., Lim T.T.*,
Dong Z.L. (2008). Application of layered double hydroxides for removal of
oxyanions: a review. Water Research 42, 1343 – 1368.
|
|
|
Water
supply
|
|
1.
|
Hu Z.-T.*, Liang Y.N., Zhao J., Zhang
Y., Yang E.-H., Chen J., Lim T.T.*
(2018). Ultra-effective integrated technologies for water disinfection with
a novel 0D-2D-3D nanostructured rGO-AgNP/Bi2Fe4O9
composite. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental 227, 548-556.
|
|
2.
|
Xiao
Y., Zhang L., Zhang W., Lim K.Y., Webster R.D., Lim T.T.* (2016). Comparative evaluation of iodoacids removal by UV/persulfate and UV/H2O2
processes. Water Research. 102, 629-639.
|
|
3.
|
Xiao
Y., Zhang L., Yue J., Webster R.D., Lim
T.T.* (2015). Kinetic modeling
and energy efficiency of UV/H2O2 treatment of
iodinated trihalomethanes Water Research 75, 259-269.
|
|
4.
|
Loo
S.L., Krantz W.B., Fane A.G., Gao Y., Hu X.*, Lim T.T.* (2015). Effect of synthesis routes on the properties
and bactericidal activity of cryogels
incorporated with silver nanoparticles. RSC Advances 5(55), 44626-44635.
|
|
5.
|
Loo
S.L., Krantz W.B., Hu X., Fane A.G.*, Lim
T.T.* (2016). Impact of solution chemistry on the properties and
bactericidal activity of silver nanoparticles decorated on superabsorbent cryogels. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 461,
104–113.
|
|
6.
|
Loo
S.L., Krantz W.B., Fane A.G., Gao Y., Lim
T.T.*, Hu X.* (2015). Bactericidal mechanisms revealed for rapid water
disinfection by superabsorbent cryogels decorated
with silver nanoparticles. Environmental Science & Technology 49(4),
2310-2318.
|
|
7.
|
Loo
S.L., Lim T.T., Krantz W.B.,
Fane A.G.*, Hu X. (2015). Potential evaluation and perspectives on using
sponge-like superabsorbent cryogels for onsite
water treatment in emergencies. Desalination and Water Treatment 53,
1506-1515.
|
|
8.
|
Xiao Y., Fan R., Zhang L., Yue J., Webster R.D., Lim T.T.* (2014). Photodegradation
of iodinated trihalomethanes in aqueous solution by UV 254 irradiation.
Water Research 49, 275-285.
|
|
9.
|
Loo
S.L., Fane A.G., Lim T.T.*,
Krantz W.B., Liang Y.N., Liu X., Hu X.* (2013). Superabsorbent cryogels decorated with silver nanoparticles as a novel
water technology for point-of-use disinfection, Environmental Science &
Technology 47(16), 9363-9371.
|
|
10.
|
Loo S.L., Krantz W.B., Lim T.T.*, Fane A.G., Hu X.* (2013). Design and synthesis of ice-templated PSA cryogels
for water purification: Towards tailored morphology and properties. Soft
Matter 9(1), 224–234.
|
|
11.
|
Loo S.L., Fane A.G.*, Krantz W.B., Lim T.T.* (2012). Emergency water supply: A review of potential
technologies and selection criteria. Water Research 46, 3125-3151.
|
|
12.
|
Goh K.H., Lim T.T.*,
Chui P.C. (2008). Evaluation of the effect of dosage, pH and
contact time on high-dose phosphate inhibition for copper corrosion control
using response surface methodology (RSM). Corrosion Science 50, 918–927.
|
|
|
|
Waste treatment
|
Waste-to-energy
|
|
1.
|
Jia J.*, Veksha A., Lim T.T., Lisak G.* (2020). In situ
grown metallic nickel from X-Ni (X=La, Mg, Sr) oxides for converting
plastics into carbon nanotubes: Influence of metal-support interaction.
Journal of Cleaner Production. In press.
|
|
2.
|
Pan Z.*, Chan W.P., Oh
W.D., Veksha A., Giannis A., Tamilselvam K.S.O., Lei J., Khairunnisa D., Wang H., Lisak G., Lim T.T.* (2020). Regenerable Co-ZnO-based
nanocomposites for high-temperature syngas desulfurization. Fuel Processing
Technology 201, 106344.
|
|
3.
|
Chan W.P.*, Sofea A.M., Veksha A., Giannis A., Lim T.T., Lisak G.* (2020). Analytical assessment of tar
generated during gasification of municipal solid waste: distribution of
GC-MS detectable tar compounds, undetectable tar residues and inorganic
impurities. Fuel 268, 117348
|
|
4.
|
Pan Z.*, Chan W.P., Veksha
A., Giannis A., Dou X., Wang H., LisakG., Lim T.T.* (2019). Thermodynamic analyses of synthetic
natural gas production via municipal solid waste gasification,
high-temperature water electrolysis and methanation. Energy Conversion and
Management 202, 112160.
|
|
5.
|
Chan W.P.*,
Veksha A., Lei X., Oh W.D., Dou X., Giannis A., Lisak G., Lim T.T.* (2019). A hot syngas
purification system integrated with downdraft gasification of municipal
solid waste. Applied Energy 237, 227-240.
|
|
6.
|
Dou X.,
Veksha A.*, Chan W.P., Oh W.D., Liang Y.N., Teoh F., Dara K., Giannis A.,
Lisak G., Lim T.T.* (2019).
Poisoning effects of H2S and HCl on the naphthalene steam
reforming and water-gas shift activities of Ni and Fe catalysts. Fuel 241,
1008-1018.
|
|
7.
|
Chan W.P.*, Veksha A.*,
Lei X., Oh W.D., Dou X., Giannis A., Lisak G., Lim T.T.* (2019).
A novel real-time
monitoring and control system for waste-to-energy gasification process
employing differential temperature profiling of a downdraft gasifier.
Journal of Environmental Management 234, 65-74.
|
|
8.
|
Veksha A.*, Giannis
A., Yuan G., Tng J., Chan W.P., Chang V.W.C.,
Lisak G., Lim T.T.* (2019).
Distribution and modeling of tar compounds
produced during downdraft gasification of municipal solid waste. Renewable
Energy 136, 1294-1303.
|
|
9.
|
Oh
W.D.*, Lei J., Veksha A., Giannis A., Chan W.P., Lisak G., Lim T.T.* (2018). Ni-Zn-based
nanocomposite loaded on cordierite-mullite honeycomb for syngas
desulfurization: Performance evaluation and regeneration studies. Chemical
Engineering Journal 351, 230-239.
|
|
10.
|
Veksha
A.*, Giannis A., Oh W.D., Chang V.W.C., Lisak G., Lim T.T.* (2018), Catalytic activities and resistance to HCl
poisoning of Ni-based catalysts during steam reforming of naphthalene.
Applied Catalysis A: General 557, 25-38.
|
|
11.
|
Oh W.D.*,
Lei J., Veksha A., Giannis A., Lisak G., Chang V.W.C., Hu X., Lim T.T. * (2018). Influence of
surface morphology on the performance of nanostructured ZnO-loaded
ceramic honeycomb for syngas desulfurization. Fuel 211C, 591-599.
|
|
Waste-to-materials
|
|
1.
|
Chanaka
Udayanga W.D., Veksha A., Giannis A., Lisak G.,
Lim T.T.* (2019). Effects
of sewage sludge organic and inorganic constituents on the properties of pyrolysis
products. Energy Conversion and Management 196,
1410-1419.
|
|
2.
|
Chanaka
Udayanga W.D., Veksha A., Giannis A., Lim T.T.* (2019). Pyrolysis
derived char from municipal and industrial sludge: impact of organic
decomposition and inorganic accumulation on the fuel characteristics of
char. Waste Management 83, 131-141.
|
|
3.
|
Oh
W.D.*, Lisak G., Liang Y.N., Veksha A., Moo J.G.S., Giannis A., Lim J.W., Lim T.T.* (2018). Insights into the thermolytic
transformation of lignocellulosic biomass waste to redox-active carbocatalyst: Durability of surface
active sites. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental 233, 120-129.
|
|
|
|
Biosolids
(sewage sludge) from wastewater treatment plant
|
|
1.
|
Chanaka Udayanga W.D., Veksha A.,
Giannis A., Lim T.T.* (2019). Pyrolysis derived char from municipal
and industrial sludge: impact of organic decomposition and inorganic
accumulation on the fuel characteristics of char. Waste Management 83,
131-141.
|
|
2.
|
Chanaka
Udayanga W.D., Veksha A., Giannis A., Lisak G., Chang V.W.C., Lim T.T.* (2018). Fate and
distribution of heavy metals during thermal processing of sewage sludge.
Fuel 226, 721–744.
|
|
3.
|
Lim T.T.*, Chu
J., Goi M.H. (2006).
Effects of cement on redistribution of trace metals and
dissolution of organics in sewage sludge and its inorganic waste-amended
products. Waste
Management 26(11), 1294-1304.
|
|
4.
|
Chu
J.*, Goi M.H., Lim T.T. (2005). Consolidation
of cement treated sewage sludge using vertical drains. Canadian Geotechnical Journal
42(2), 528-540.
|
|
5.
|
Lim T.T.*, Chu J., Goi M.H. (2004). Assessment of heavy metals
leachability in clay-amended sewage sludge stabilized with cement for use
as fill material. Journal
of Residuals Science & Technology 1(3), 157-164.
|
|
|
|
MSW
incinerator ashes
|
|
1.
|
Lim T.T.*, Tay
J.H., Tan L.C., Choa V., Teh C.I. (2004). Changes
in mobility and speciation of heavy metals in clay-amended incinerator fly
ash. Environmental
Geology 47(1), 1-10.
|
|
2.
|
Lim T.T.*, Tay
J.H., Wang J.Y. (2001).
MSW fly ash treatment by acid and chelating agent for reuse. Proc., 17th
Int. Conf. On Solid Waste Technology and Management, Philadelphia, U.S.A.,
pp530-538.
|
Environmental remedial technologies
|
Oil spill cleanup
|
|
1.
|
Chaturabong
P.*, Lim T.T., Wong Y.D. (2018).
Effective surface treatment techniques for refinishing oil-stained road
surface. Construction & Building Materials 159, 64-72.
|
|
2.
|
Chen B., Ma Q., Tan C., Lim T.T., Huang L., Zhang H. (2015). Carbon-based sorbents with
three-dimensional architectures for water remediation. Small 11(27),
3319-3336.
|
|
3.
|
Lim
T.T.* and Huang X.F. (2007). Evaluation of kapok (Ceiba pentandra (L.) Gaertn.) as a
natural hollow hydrophobic-oleophilic fibrous sorbent for oil spill cleanup. Chemosphere 66(5), 955-963.
|
|
4.
|
Lim T.T.* and Huang X.F. (2007). Evaluation of
hydrophobicity/oleophilicity of kapok and its performance in oily water
filtration: comparison of raw and solvent-treated fibers.
Industrial Crops and Products 26(2), 125–134.
|
|
5.
|
Huang X.F., Lim T.T.* (2006). The performance and mechanism of hydrophobic-oleophilic
kapok filter for oil/water separation. Desalination 190, 295–307.
|
|
6.
|
Lim
T.T.*, Huang X.F. (2006). In-situ oil/water separation using
hydrophobic-oleophilic fibrous wall: a lab-scale feasibility study for
groundwater cleanup. Journal of Hazardous
Materials B137, 820-826.
|
|
In the project of oil
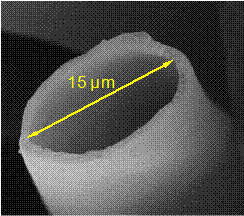
removal from water, my research group investigated oil removal from oily
water, simulated aquifer, and oil spills on surface water using a kind of
natural plant product which has hydrophobic-oleophilic property. The
fibrous product has a hollow structure with large lumen. It is known as
kapok by the native people living in the Southeast Asia. It is cheaper and
has higher oil absorption capacity compared to cotton due to its
lightweight and high specific volume.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Oil sorption by packed sorbent at
various packing densities
|
|
|
|
|
Contaminants removal from
contaminated soils
|
|
1.
|
Lim
T.T.*, Chui P.C., Goh K.H. (2005). Process evaluation for
optimization of EDTA use and recovery for heavy metal removal from a
contaminated soil.
Chemosphere 58(8), 1031-1040.
|
|
2.
|
Lim
T.T.*, Tay J.H., Wang J.Y. (2004). Chelating-agent enhanced heavy metal extraction from a contaminated acidic soil. Journal
of Environmental Engineering, ASCE, 130, 59-66.
|
|
3.
|
Goh K.H., Lim T.T.* (2005). Arsenic extractability in a fine
soil fraction and influence of various anions on its mobility in subsurface
environment. Applied
Geochemistry 20(2), 229-239.
|
|
4.
|
Lim T.T.*, Goh K.H. (2005). Selenium
extractability from a contaminated fine soil fraction: implication on soil cleanup. Chemosphere 58(1), 91-101.
|
|
|
International collaborations
(past and present)
|
|
·
Department of Civil
Engineering, Monash University, Victoria, Australia
|
|
·
School of Environmental Engineering (ENVENG),
Technical University of Crete, Chania, Greece
|
|
·
School of Chemical Sciences, Universiti Sains Malaysia,
Penang, Malaysia
|
|
·
School of Environment, Harbin
Institute of Technology, Harbin, China
|
|
·
School of Material Science and
Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China
|
|
·
Key Laboratory of Coal Science
and Technology of Shanxi Province and Ministry of Education, Taiyuan
University of Technology, Taiyuan, China
|
|
·
College of Environment,
Zhejiang University of Technology, Hangzhou, China
|
|
·
School of Environmental
Science and Engineering, Huazhong University of Science and Technology,
Wuhan, China
|
|
·
School of Environmental and
Chemical Engineering, Shanghai University, Shanghai, China
|
|
·
Key Laboratory of Drinking
Water Science and Technology, Research Center for
Eco-Environmental Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chinese
Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China
|
|
·
Key Lab of Groundwater
Resources and Environment, Ministry of Education, Jilin University,
Changchun, China
|
|
·
Department of Chemical and
Biological Engineering, University of Colorado, Boulder, Colorado, USA
|
|
·
School of Chemical
Engineering, University of New South Wales, Sydney, New South Wales,
Australia
|
|
·
School of Civil and
Environmental Engineering, Pusan National University, Busan, Republic of
Korea
|
|
·
School of Civil Engineering,
King Mongkut’s Institute of Technology Ladkrabang, Bangkok, Thailand
|
|
·
Department of Civil &
Environmental Engineering, Stanford University, Palo Alto, California, USA
|
|
|
|
