-
Plasmonic Vesicles of Amphiphilic Gold Nanocrystals: Self-Assembly and External-Stimuli-Triggered Destruction
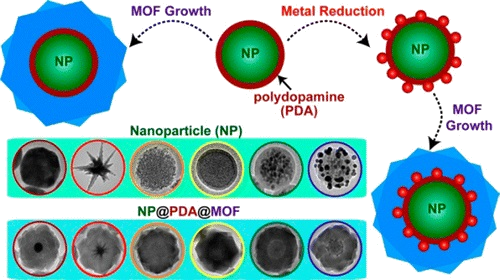
We report a versatile strategy based on the use of multifunctional mussel-inspired polydopamine for constructing well-defined single-nanoparticle@metal-organic framework (MOF) core-shell nanohybrids. The capability of polydopamine to form a robust conformal coating on colloidal substrates of any composition and to direct the heterogeneous nucleation and growth of MOFs makes it possible for customized structural integration of a broad range of inorganic/organic nanoparticles and functional MOFs. Furthermore, the unique redox activity of polydopamine adds additional possibilities to tailor the functionalities of the nanohybrids by sandwiching plasmonic/catalytic metal nanostructures between the core and shell via localized reduction. The core-shell nanohybrids, with the molecular sieving effect of the MOF shell complementing the intrinsic properties of nanoparticle cores, represent a unique class of nanomaterials of considerable current interest for catalysis, sensing, and nanomedicine.
-
Coating Graphene Paper with 2D-Assembly of Electrocatalytic Nanoparticles: A Modular Approach toward High-Performance Flexible Electrodes
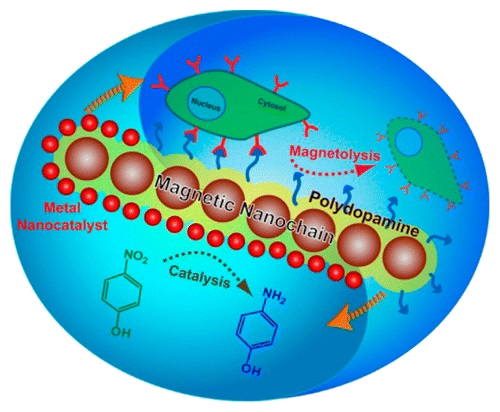
We present a new strategy, built upon the use of mussel-inspired polydopamine (PDA), for constructing multifunctional nanochains of magnetic nanoparticles. One key finding is that self-polymerization of PDA around magnetically aligned nanoparticles affords robust rigid magnetic nanochains with versatile reactivity imparted by PDA. In particular, we have shown that loading of metal nanoparticles on the nanochains via localized reduction by PDA gave rise to magnetically recyclable, self-mixing nanocatalysts. Surface coupling of PDA with nucleophilic thiol and amine groups via Michael addition and/or Schiff base reactions, on the other hand, enabled easy bioconjugation of targeting ligands such as DNA aptamer for specific recognition of the nanochains to cancer cells, which led to magnetolysis of the cancer cells in a spinning magnetic field. The PDA-enabled strategy allows for flexible selection of magnetic building blocks and postsynthesis functionalization, which are of considerable interest for a wide spectrum of chemical and biomedical applications.
-
Responsive Plasmonic Assemblies of Amphiphilic Nanocrystals at Oil Water Interfaces
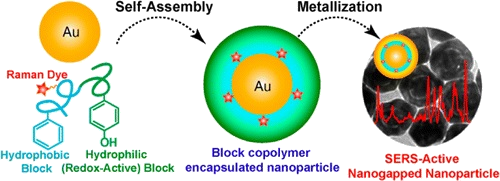
We report a new strategy to synthesize core-shell metal nanoparticles with an interior, Raman tag-encoded nanogap by taking advantage of nanoparticle-templated self-assembly of amphiphilic block copolymers and localized metal precursor reduction by redox-active polymer brushes. Of particular interest for surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) is that the nanogap size can be tailored flexibly, with the sub-2 nm nanogap leading to the highest SERS enhancement. Our results have further demonstrated that surface functionalization of the nanogapped Au nanoparticles with aptamer targeting ligands allows for specific recognition and ultrasensitive detection of cancer cells. The general applicability of this new synthetic strategy, coupled with recent advances in controlled wet-chemical synthesis of functional nanocrystals, opens new avenues to multifunctional core-shell nanoparticles with integrated optical, electronic, and magnetic properties.
|