Multimedia Signal Processing
 H. Yi, D. Rajan and L. T. Chia, A ZGPCA algorithm for subspace estimation, ICME, Beijing, 2007.
H. Yi, D. Rajan and L. T. Chia, A ZGPCA algorithm for subspace estimation, ICME, Beijing, 2007. 

Deepu Rajan
Associate
Professor
College of Computing and Data Science, Nanyang Technological University

| HOME | RESEARCH | TEACHING | BIOGRAPHY | LINKS |

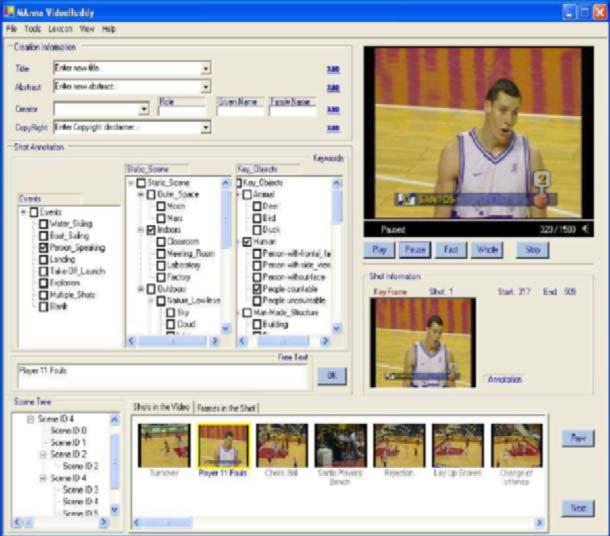 |
| Video annotation tool interface. User selects a video to be annotated. The algorithm performs shot
boundary detection, key frame extraction and builds the scene tree
shown in the bottom left part of the interface. The key frames from
each shot are shown as thumbnail images on the right panel. The user
can navigate the ‘‘scene tree’’ and select interested scene node for
annotation. |


| Near-duplicate Image Retrieval |